What Is Functional Nutrition: Unlocking Your Health Potential
Functional Nutrition is a holistic approach to health. It focuses on the unique needs of each person.
In our fast-paced world, many people experience health issues that standard diets and treatments can’t fix. Functional Nutrition steps in to address these deeper problems. It looks at how our bodies work and how we can support them through food and lifestyle choices.
This approach considers genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors to tailor nutrition plans to each individual. It’s about finding the root cause of health issues and addressing them with the right nutrients. By focusing on the whole person, Functional Nutrition helps improve overall well-being, making it a powerful tool for those seeking better health.

What Is Functional Nutrition
Functional Nutrition is an approach to health that focuses on the whole person, not just isolated symptoms. It aims to understand the root causes of health issues and address them through personalized dietary and lifestyle changes. This method looks beyond traditional nutrition, incorporating aspects of functional medicine to promote overall well-being.
What Is Functional Nutrition?
Functional Nutrition is a holistic approach to health and wellness. It considers how different systems in the body interact with each other. Instead of treating symptoms, it seeks to identify and address the underlying causes of health problems. This method emphasizes the importance of a balanced diet, rich in nutrients, to support the body’s natural functions. Functional Nutrition practitioners often use a personalized approach. They take into account individual differences in genetics, environment, and lifestyle. This means that what works for one person may not work for another. The goal is to create a tailored plan that meets each person’s unique needs.
Key Principles Of Functional Nutrition
Functional Nutrition is based on several key principles:
- Bio-Individuality: Each person has unique nutritional needs.
- Whole Foods: Emphasis on unprocessed, natural foods.
- Root Cause Resolution: Focus on identifying and addressing the underlying causes of health issues.
- Systemic Approach: Understanding how different body systems interact and affect each other.
Benefits Of Functional Nutrition
Functional Nutrition offers numerous benefits:
- Improved digestion and gut health
- Enhanced energy levels
- Better management of chronic conditions
- Personalized dietary recommendations
- Overall improved well-being
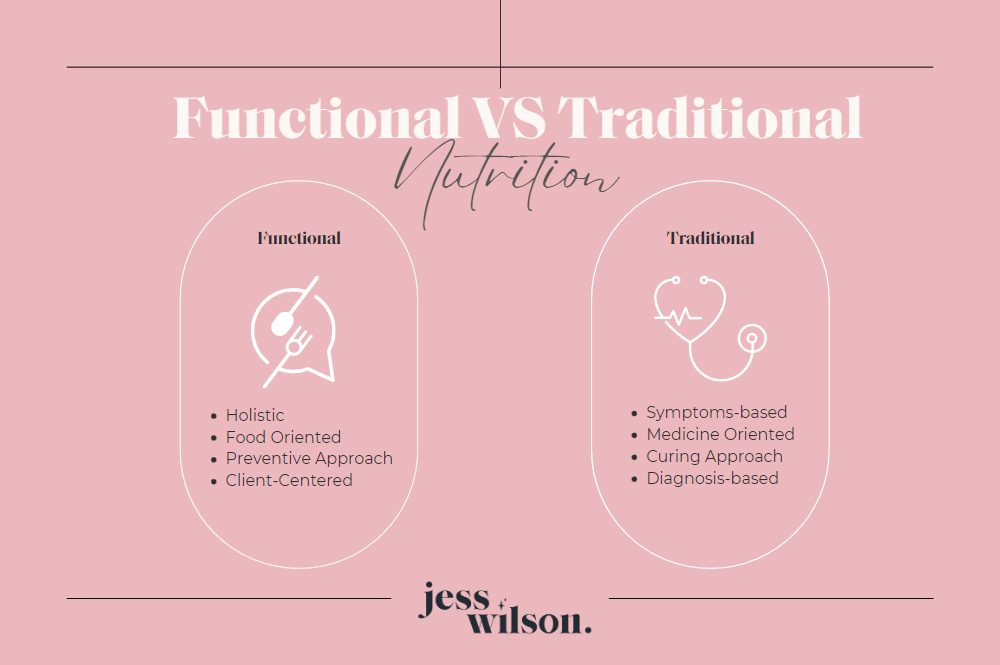
How Functional Nutrition Differs From Traditional Nutrition
Traditional Nutrition often focuses on dietary guidelines for the general population. It provides broad recommendations based on average needs. Functional Nutrition, on the other hand, is personalized. It considers individual factors such as:
| Traditional Nutrition | Functional Nutrition |
|---|---|
| General dietary guidelines | Personalized dietary plans |
| Focus on symptoms | Focus on root causes |
| One-size-fits-all approach | Individualized approach |
Functional Nutrition aims to go deeper. It looks at the interconnectedness of the body’s systems. By understanding these connections, it provides a more comprehensive approach to health.
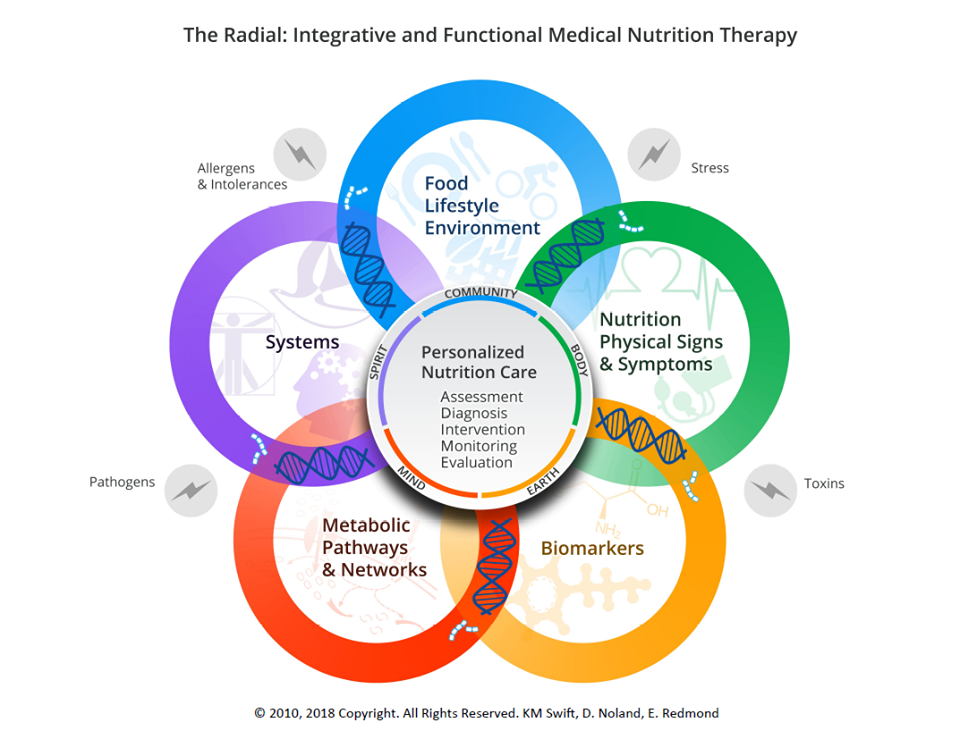
Core Principles
Functional nutrition is a personalized approach to health that focuses on the root causes of disease. It emphasizes the importance of whole foods and lifestyle changes. The core principles of functional nutrition guide this approach, ensuring a holistic and individualized care for each person.
Holistic Approach
Functional nutrition takes a holistic approach to health. It looks at the whole person, not just symptoms. This means considering physical, mental, and emotional health. Key aspects of the holistic approach include:
- Nutrition
- Exercise
- Stress management
- Sleep
For example, a person experiencing chronic fatigue might need more than just a change in diet. They could benefit from:
| Aspect | Recommendations |
|---|---|
| Nutrition | Whole foods, reduce sugar intake |
| Exercise | Regular, moderate activity |
| Stress Management | Meditation, deep breathing |
| Sleep | Consistent sleep schedule, relaxing bedtime routine |
By addressing all these areas, functional nutrition helps achieve better health. It is not just about what you eat. It is about creating a balanced lifestyle.
Individualized Care
Another core principle is individualized care. This means recognizing that everyone is unique. Each person has different needs and health issues. Individualized care includes:
- Personalized nutrition plans
- Specific supplement recommendations
- Tailored exercise programs
- Customized stress management techniques
For instance, two people with the same condition might need different treatments. One might need more vitamin D, while another needs more magnesium. This is why functional nutrition practitioners often use detailed health histories and tests. These tests might include:
- Blood tests
- Genetic testing
- Allergy tests
- Hormone level assessments
With this information, a unique plan is created. This ensures each person gets what they need for optimal health. Individualized care respects that everyone is different. It avoids one-size-fits-all solutions.
Role Of Nutrients
Functional Nutrition looks at how food affects health. It focuses on the role of nutrients in the body. Nutrients are vital for growth, energy, and overall well-being. Understanding their role helps in making better food choices.
Essential Nutrients
Essential nutrients are compounds the body cannot produce on its own. They are crucial for health. We must get them from our diet. These nutrients include:
- Carbohydrates
- Proteins
- Fats
- Vitamins
- Minerals
- Water
Carbohydrates provide energy. Our body uses them for fuel. Whole grains, fruits, and vegetables are good sources. Proteins are the building blocks of our body. They help in tissue repair and muscle building. Sources include meat, beans, and nuts. Fats are essential for brain health. They also help in absorbing vitamins. Healthy fats come from fish, avocados, and olive oil. Vitamins and minerals support various bodily functions. They boost the immune system and ensure proper growth. Fruits and vegetables are rich in these nutrients. Water is vital for hydration. It aids in digestion and helps in nutrient transport. We should drink enough water daily.
Micronutrients Vs. Macronutrients
Nutrients are classified into two categories: micronutrients and macronutrients. Both are essential but serve different roles. Macronutrients are needed in larger amounts. They include carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
- Carbohydrates: 4 calories per gram
- Proteins: 4 calories per gram
- Fats: 9 calories per gram
These provide energy and support growth and repair. Micronutrients are needed in smaller amounts. They include vitamins and minerals.
- Vitamins: Essential for metabolism
- Minerals: Important for bone health, fluid balance
Though needed in small amounts, they are crucial for preventing diseases and maintaining health. Here is a simple table to differentiate between the two:
| Type | Needed Amount | Examples | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Macronutrients | Large Amounts | Carbohydrates, Proteins, Fats | Energy, Growth, Repair |
| Micronutrients | Small Amounts | Vitamins, Minerals | Metabolism, Bone Health |
Balancing both types ensures optimal health. It helps in energy production, growth, and disease prevention.
Gut Health
Functional nutrition looks at food as a way to achieve better health. It focuses on the unique needs of the individual. One key area is gut health. A healthy gut is essential for overall wellness. It affects digestion, absorption, immunity, and even mood. Understanding gut health can help you make better dietary choices and improve your well-being.
Microbiome Impact
The microbiome is a community of trillions of bacteria, viruses, and fungi living in your gut. These microorganisms play a vital role in your health. They help break down food, produce vitamins, and protect against harmful bacteria. Having a diverse microbiome is important. A wide variety of gut bacteria promotes better health. It helps your body fight infections and reduces inflammation. Here are some factors that influence your microbiome:
- Diet: Eating a variety of fiber-rich foods nourishes your gut bacteria.
- Antibiotics: Frequent use can harm good bacteria.
- Probiotics: Consuming probiotic-rich foods like yogurt can boost good bacteria.
- Stress: High stress levels can negatively affect your gut.
Maintaining a healthy microbiome supports overall health. It can improve your digestion and boost your immune system.
Digestion And Absorption
Digestion is the process where your body breaks down food into nutrients. Absorption is how these nutrients enter your bloodstream. Both are crucial for your health. Functional nutrition aims to optimize these processes. Several factors can affect digestion and absorption:
- Chewing: Properly chewing food aids digestion. It makes nutrients easier to absorb.
- Stomach Acid: Adequate stomach acid levels help break down food. Low levels can hinder nutrient absorption.
- Enzymes: Digestive enzymes from the pancreas and small intestine are essential. They help break down proteins, fats, and carbohydrates.
- Gut Lining: A healthy gut lining ensures nutrients are absorbed effectively. Damage to this lining can lead to malabsorption.
Functional nutrition recommends eating whole foods. These are easier to digest and absorb. It also suggests avoiding processed foods. They can disrupt digestion and harm your gut lining. By focusing on gut health, functional nutrition helps improve digestion and nutrient absorption. This leads to better overall health and well-being.
Chronic Disease Prevention
Functional Nutrition focuses on the root causes of health issues and uses food and nutrients to support the body’s natural processes. One of its key benefits is chronic disease prevention. By addressing underlying imbalances, functional nutrition helps reduce the risk of long-term health issues. It looks at how diet and lifestyle choices impact overall health and wellness.
Inflammation Reduction
Chronic inflammation is a major contributor to many diseases. Conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and arthritis are linked to ongoing inflammation. Functional nutrition aims to reduce this inflammation through specific dietary choices. Here are some ways to reduce inflammation with functional nutrition:
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts. These fats help lower inflammation.
- Antioxidant-Rich Foods: Berries, leafy greens, and nuts are rich in antioxidants. They fight off free radicals and reduce inflammation.
- Spices: Turmeric and ginger have anti-inflammatory properties. Adding these spices to meals can help reduce inflammation.
It is also important to avoid foods that cause inflammation. These include:
- Refined Sugars: Found in sodas, candies, and baked goods.
- Trans Fats: Present in many fried and processed foods.
- Excessive Alcohol: Can increase inflammation in the body.
Making these dietary changes can significantly impact inflammation levels. Over time, this reduces the risk of chronic diseases.
Metabolic Balance
Metabolic balance is crucial for maintaining a healthy body weight and preventing diseases. Metabolism involves all the chemical reactions in the body that maintain life. Functional nutrition supports metabolic balance through personalized dietary plans. Key strategies for achieving metabolic balance include:
- Balanced Macronutrients: Ensure a proper balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in meals. This helps regulate blood sugar levels and maintain energy.
- Regular Meals: Eating at regular intervals prevents blood sugar spikes and crashes.
- Whole Foods: Choose whole, unprocessed foods. They provide essential nutrients without added sugars and unhealthy fats.
Some foods that support metabolic health include:
| Food | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Avocados | Rich in healthy fats and fiber |
| Leafy Greens | Low in calories, high in nutrients |
| Lean Proteins | Support muscle health and metabolism |
By focusing on these dietary principles, functional nutrition helps maintain a balanced metabolism. This reduces the risk of metabolic disorders like obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Personalized Nutrition Plans
Functional Nutrition is a holistic approach to health. It focuses on understanding the unique needs of each individual. Personalized Nutrition Plans are a key component of this approach. These plans tailor dietary recommendations to suit each person’s specific health needs and goals. This personalized approach can help address various health concerns, improve well-being, and support long-term health. Let’s explore how these plans are crafted and monitored.
Assessments And Goals
Creating a Personalized Nutrition Plan begins with thorough assessments. These assessments help understand your current health status and nutritional needs. Here are some key components:
- Health History: Reviewing past medical conditions, surgeries, and family health history.
- Dietary Habits: Analyzing current eating patterns, food preferences, and intolerances.
- Lifestyle Factors: Considering sleep patterns, stress levels, physical activity, and work environment.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests and other diagnostics to check for deficiencies or imbalances.
After gathering this information, specific goals are set. These goals are realistic and tailored to your needs. They may include:
- Weight Management: Achieving or maintaining a healthy weight.
- Improving Digestion: Addressing issues like bloating or constipation.
- Boosting Energy: Increasing daily energy levels.
- Enhancing Immunity: Strengthening the immune system.
These goals guide the creation of a nutrition plan. The plan includes specific dietary recommendations, supplement suggestions, and lifestyle changes. It is a roadmap to better health.
Tracking Progress
Tracking progress is essential for the success of Personalized Nutrition Plans. Regular monitoring helps ensure that you are on the right path. Here are some methods used to track progress:
- Follow-up Appointments: Regular check-ins with your nutritionist to review progress and make adjustments.
- Food Diaries: Keeping a record of daily food intake to identify patterns and areas for improvement.
- Biomarker Testing: Periodic blood tests to monitor nutrient levels and health markers.
- Body Measurements: Tracking changes in weight, waist circumference, and body fat percentage.
Consistent tracking allows for timely adjustments to the plan. For instance, if a particular food is causing discomfort, it can be replaced. If energy levels are not improving, additional nutrients might be introduced. This iterative process ensures that the nutrition plan remains effective and aligned with your health goals. In addition to professional monitoring, self-monitoring is encouraged. Using apps or journals to track meals and symptoms can provide valuable insights. This collaborative approach between you and your nutritionist fosters a sense of ownership and accountability. It also enhances the likelihood of achieving your health goals.
Lifestyle Factors
Functional nutrition looks at the whole person. It focuses on how our lifestyle affects our health. Lifestyle factors like stress and sleep play a big role. They can impact our well-being and how our body works. Let’s explore two key lifestyle factors: stress management and sleep quality.
Stress Management
Stress can harm our health. It can cause problems like headaches, high blood pressure, and even heart disease. Managing stress is important for good health. Here are some ways to manage stress:
- Exercise: Physical activity helps reduce stress hormones. It also increases feel-good chemicals called endorphins.
- Meditation: This practice helps calm the mind. It can reduce anxiety and improve focus.
- Healthy Eating: A balanced diet supports the body. It provides the nutrients needed to cope with stress.
- Time Management: Organizing your day can reduce stress. It helps you feel more in control.
Stress management techniques can vary. What works for one person might not work for another. Here’s a simple table summarizing these techniques:
| Technique | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Exercise | Reduces stress hormones, increases endorphins |
| Meditation | Calms the mind, reduces anxiety |
| Healthy Eating | Supports the body, provides nutrients |
| Time Management | Reduces stress, increases control |
Sleep Quality
Good sleep is crucial for health. It helps the body repair and recharge. Poor sleep can lead to many issues. These include weight gain, mood swings, and weakened immunity. Here are some tips for better sleep:
- Create a Routine: Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day. This helps regulate your body’s clock.
- Limit Screen Time: Avoid screens before bed. The blue light from devices can disrupt sleep.
- Healthy Diet: Avoid heavy meals and caffeine before bed. These can keep you awake.
- Relaxation Techniques: Practices like reading or taking a bath can help you unwind.
Sleep quality affects our overall health. Making small changes can improve your sleep. This, in turn, can boost your health and well-being.
Future Of Functional Nutrition
Functional Nutrition focuses on how food affects our health at the cellular level. It looks at how different foods can help or harm our bodies. This approach is personalized and considers each person’s unique needs. Looking ahead, the future of Functional Nutrition is promising. It aims to blend science with personal health to improve lives. It also looks to collaborate with traditional medicine for better outcomes.
Research Trends
Research in Functional Nutrition is growing. Scientists are exploring how food can prevent and treat diseases. They study how different nutrients affect our genes and cells. This is called Nutrigenomics. Here are some key research trends:
- Nutrigenomics: Examines how food and genes interact.
- Microbiome Studies: Studies how gut bacteria affect health.
- Personalized Nutrition: Tailors diets based on individual needs.
Research shows that a healthy diet can lower the risk of chronic diseases. For example, eating more fruits and vegetables can reduce heart disease and diabetes risk. Scientists also study how food affects mental health. They find that a balanced diet can improve mood and reduce anxiety. A table summarizing research trends:
| Research Area | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Nutrigenomics | Study of food and gene interaction | Personalized diet plans |
| Microbiome Studies | Study of gut bacteria | Improved digestion and immunity |
| Personalized Nutrition | Customized diets | Better health outcomes |
Integration With Conventional Medicine
Functional Nutrition and conventional medicine can work together. This integration can offer a more comprehensive approach to health. Here are some ways they can collaborate:
- Patient-Centered Care: Combining nutrition and medicine for personalized treatment.
- Chronic Disease Management: Using diet to manage and prevent chronic illnesses.
- Preventive Health: Focusing on diet to prevent diseases before they start.
Doctors and nutritionists can work together to create better treatment plans. For instance, a patient with diabetes can benefit from medical treatment and a tailored diet plan. This can help control blood sugar levels more effectively. Another example is heart disease. A combination of medication and a heart-healthy diet can improve outcomes. Functional Nutrition can also help in recovery. After surgery, a nutritious diet can speed up healing. Medical professionals can use this approach to enhance patient care. It makes the treatment more effective and holistic. Overall, the future of Functional Nutrition looks bright. Its integration with conventional medicine promises better health for everyone.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Functional Nutrition?
Functional nutrition focuses on personalized dietary choices. It aims to improve overall health and well-being by addressing specific nutritional needs and imbalances.
How Does Functional Nutrition Work?
Functional nutrition works by assessing individual health conditions. It identifies nutritional deficiencies and tailors diet plans to support optimal health and function.
Is Functional Nutrition Evidence-based?
Yes, functional nutrition is evidence-based. It relies on scientific research and clinical studies to guide dietary recommendations and interventions.
Can Functional Nutrition Help With Chronic Diseases?
Functional nutrition can help manage chronic diseases. It addresses root causes and supports the body’s natural healing processes through targeted nutrition.
Conclusion
Functional nutrition focuses on personalized health and balanced eating. It considers the unique needs of each individual. This approach aims to improve well-being naturally. By choosing whole foods, you support your body’s functions. Understanding your body’s needs helps in making better food choices.
Remember, small changes can make a big difference. Embrace functional nutrition for a healthier lifestyle. Take the first step today. Your body will thank you.




